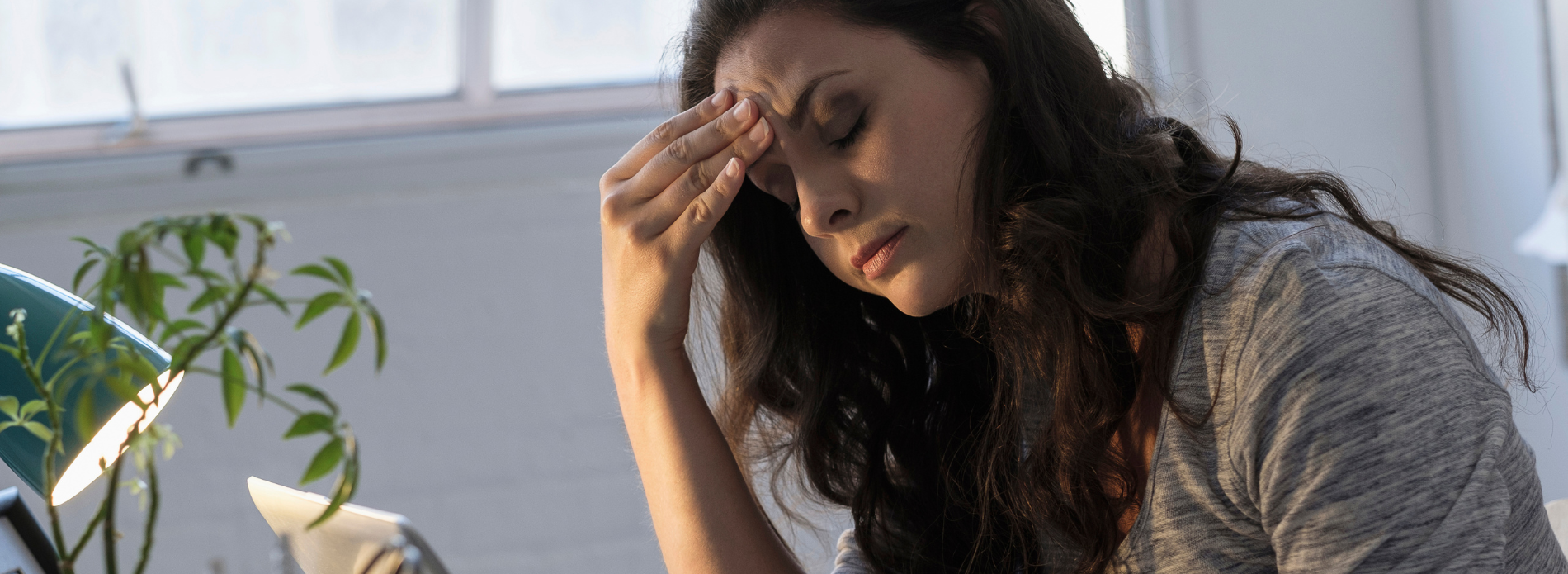
Migraines can affect different aspects of someone’s life, can vary in intensity, occur more frequently for some than others and can be triggered by a range of factors or have no found cause at all.
Globally, 20.7% of women suffer from migraines compared to 9.7% of men. With hormonal differences, differences in brain structure and neuronal pathways thought to be contributing factors as to why they’re more prevalent in women.1
We’re looking at the different stages of migraines, what some of the triggers could be and what can be done to help treat them.
What is a migraine?
Migraines are a long-term health condition, commonly described as a severe throbbing pain in the head, usually on one side. But they can be a whole-body experience, lasting for anything between 2 hours and 3 days.2
The frequency differs for everyone, some might get two to four per month whereas others can experience migraines every few days, while others may get them once or twice a year.
It’s estimated that 190,000 migraine attacks occur every day in the UK, and over three quarters of people who get migraine have at least one attack each month.3
Symptoms of a migraine
Symptoms are different for everyone but can include:
- head pain,
- sight difficulties e.g. seeing flashing lights,
- sensitivity to light, sounds and smells,
- fatigue,
- nausea and being sick.
Most sufferers report a ‘prodrome period’ where they experience some of the symptoms above before the head pain starts. Some other symptoms during this phase can also include mood swings, food cravings and stiffness of the neck.4
How do I know if it’s a headache or migraine?
Generally, it’s thought that there are defined stages of a migraine which helps to determine if it’s a headache or an incoming migraine attack. The Migraine Trust advise that “not everyone will experience all of the symptoms of each stage and the stages can overlap.” But “it is these stages and their symptoms that distinguish a migraine from a headache.”5
- Premonitory stage – this is also known as the ‘prodrome stage’, as mentioned above. It’s where some physical and mental changes happen and is thought to be the first warning that a migraine is incoming.
- Aura – this phase is focused on sensory disturbances and is another warning sign that a migraine attack is coming. Sufferers would usually see flashing lights, blind spots or temporary blindness but it can be numbness or tingling in the body, dizziness or changes in speech. These symptoms usually happen before head pain – building up over 5 minutes and lasting up to an hour.
- The headache/the main attack – this can be moderate to severe head pain, normally a throbbing on one side that is made worse by movement. Nausea and vomiting can happen at this stage, and you may feel sensitive to light, sound and smell. Painkillers work best when taken early in this stage.6
- Resolution – the attacks slowly start to go in this phase and usually sufferers would sleep to help end the attack, or in some cases vomiting helps.
- Postdrome stage – this is the recovery phase where many feel drained whilst they wait to ‘get back to normal’. Some feel tired or the opposite and in fact feel full of energy, whilst others feel confused and generally unwell.
Without aura
These are the most common types of migraine and are attacks that contain no warning signs. They usually start with the head pain and can last up to three days if not treated and have the same symptoms of the ‘main attack’ described above.
What causes migraines?
It’s widely thought that migraines are caused by abnormal brain activity which affects nerve signals, chemicals and blood vessels. It’s likely that genetic factors cause the abnormal brain activity and you're more likely to get them if you have a close family member who gets them too.7
But, if you’re sensitive to migraines, certain factors can trigger them.
Triggers
Environment – lack of sleep, stress, or even lighting and temperature can be a trigger.
Diet – sufferers are often advised to keep a food diary to help determine if certain types of food trigger an attack. Foods such as dairy, alcohol, caffeine and chocolate are thought to be some of the more common triggers, but it varies from person-to-person.
Hormones – women are more likely to suffer from migraines due to their menstrual cycles and changing hormone levels.
What can I do to treat a migraine?
Treatment for migraines depends on the type, your symptoms, the severity and how regularly you get them.
Painkillers and anti-sickness medication can help relieve symptoms but if you get regular attacks, your GP may prescribe preventative treatments which can include blood pressure and anti-seizure medications. During an attack, some people find lying in a dark room helpful.
It’s also worth looking at any lifestyle factors that may be contributing to the attacks – lack of sleep or exercise, diet or stress. It can help to keep a diary of when the migraines occur so you can potentially find any patterns.
For some sufferers acupuncture has been shown to help, although not all GP surgeries offer this, and it would have to be sought privately.
Unfortunately, there is no current cure for migraines, but people tend to find the attacks get less severe over time.
References
- Sex and gender differences in migraines – National Library of Medicine
- Migraine – NHS
- How does it affect people? – The Migraine Trust
- Migraine vs. Headache: How to Tell the Difference – Penn Medicine
- Stages of a migraine attack – The Migraine Trust
- Stages of a migraine attack – The Migraine Trust
- Causes of migraines – NHS